Hmm. Never been to Vegas before: seems designed to bring out the New England Puritan in me. I’ll pass on opulence, thank you very much…

SAP HANA/ IoT Conference
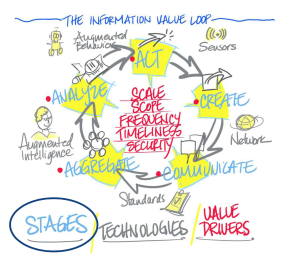
Up front, very interested in a handout from Deloitte, “Beyond Linear,” which really is in line with speech I’ll give here tomorrow on the IoT “Essential Truths,” in which one of my four key points will be that we need to abandon the old, linear flow of data for a continuous cyclical one. According to Deloitte’s Jag Bandia,
“Among users with a complete, 360-degree view of relevant data for each specific process can help avoid missed opportunities. The ‘all data’ approach means relevant data can and should come from anywhere — any application, any system, any process — not just the traditional channels associated with the process.”
Bravo!
First speaker: SAP Global Customers Operations CTO Ifran Khan:
- “digital disruption”: catalyst for change & imperative to go digital.
- digression about running going digital (I put in my 30 minutes this morning!!!), creating a totally new way of exercising (fits beautifully with “Smart Aging“!)
- new macro tech trends are enabling digitalizations: hyper-connectivity, super computing, cloud computing, smart world, and cybersecurity (horrifying stat about how many USB sticks were left in dry cleaning!)
- those who don’t go digital will go under…. (like John Chambers’ warning about IoT).
- new opportunities in wide range of industries
- need new digital architectures — “driving locality of data, integrated as deep as possible into the engine.
- HOLY COW! He starts talking about a circular, digitally-centered concept, with a buckyball visual. Yikes: great minds think alike.
- sez HANA allows a single platform for all digital enterprise computing.
- running things in real-time, with no latency — music to my ears!
Jayne Landry, SAP:
- too few in enterprise have real-time access to analytics — oh yeah!
- “analytics for everyone”
- “own the outcome”
- “be the one to know”
- SAP Cloud for Analytics — “all analytics capabilities in one product.” real-time, embedded, consumer-grade user experience, cloud-based. Looking forward to seeing this one!
- “Digital Boardroom” — instant insight. Same info available to board also available to shopfloor — oh yeah — democratizing data!
Very funny bit by Ty Miller on using SAP Cloud for Analytics to analyze Area 51 data. Woo Woo!
Ifran Khan again:
- how to bring it to the masses? Because it’s expensive and difficult to maintain on the premises, extend and build in cloud! Add new “micro services” to SAP HANA cloud platform: SAP Application Integration, Tax Service, Procurement, Customer Engagement, Predictive, and, ta da, IoT.
- video of Hamburg Port Authority. Absolutely love that and what they’re doing with construction sites!
Jan Jackman, IBM:
- customers want speed. Cloud is essential. IBM & HANA are partners in cloud…
This guy is sooo neat: Michael Lynch, IoT Extended Supply Chain for SAP (and former opera student!):
- “Connecting information, people, and things is greatest resource ever to drive insightful action.”
- “big deal is the big data processing potential is real & chips are cheaper, so you can build actual business solutions”
- STILL gmbh (forklifts) great example!
- phase 1: connect w/ billions of internet-enabled things to gain new insights
- phase II: transform the way you make decisions and take action
- phase III: re-imagine your customer’s experience.
- they do design thinking workshops — would luv one of those!
- great paradigm shift: Hagleitner commercial bathroom supplies
- Kaeser compressors: re-imaging customer service
- working with several German car companies on enabling connected driving
- once again, the Hamburg Port Authority!!
SAP’s strategy:
- offers IoT apps. platforms, and facilitates extensions of IoT solutions
- work closely with Siemens: he’s talked with them about turbine business.
- SAP has several solutions for IoT
- Cloud-based predictive maintenance!
- “social network for assets”: Asset Intelligence Network
- They did the Harley York PA plant! — one line, 21-day per bike to 6 hrs. (displays all around the plant with KPIs)
- 5 layers of connectivity in manufacturing “shop floor to top floor” SAP Connected Manufacturing
- They have a IoT Starter Kit — neat
- SAP Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence
- SAP Plant Connectivity
- SAP Event Stream Processor
- SAP MobiLink
- SAP SQL Anywhere/SAP ultralite
- 3rd Party IoT Device Cloud (had never heard of “device cloud” concept — specialize in various industry verticals).
“Becoming an Insight-Driven Organization” Speakers: Jag Bandla and Chris Dinkel of Deloitte.
- Deloitte is using these techniques internally to make Deloitte “insight-driven”
- “an insight-driven organization (IDO) is one which embeds analysis, data, and reasoning into every step of the decision-making process.” music to my ears!
- emphasis on actionable insight
- “when humans rely on their own experiences and knowledge, augmented by a stream of analytics-driven insights, the impact on value can be exponential”
- benefits to becoming an IDO:
- faster decisions
- increased revenue
- decreased cost of decision making
- challenges:
- lack of proper tech to capture
- oooh: leaders who don’t understand the data…
- 5 enabling capabilities:
- strategy
- people
- process
- data
- tech
- developing vision for analytics
- Key questions: (only get a few..)
- what are key purchase drivers for our customers?
- how should we promote customer loyalty?
- what customer sentiments are being expressed on social media?
- how much should we invest in innovation?
- Value drivers:
- strategic alignment
- revenue growth
- cost reduction
- margin improvement
- tech
- regulation/compliance
- Organize for success (hmm: I don’t agree with any of these: want to decentralize while everyone is linked on a real-time basis):
- centralized (don’t like this one, with all analyzed in one central group.. decentralize and empower!)
- consulting: analysts are centralized, but act as internal consultants
- center of excellence: central entity coordinates community of analysts across company
- functional: analysts in functions such as marketing & supply chain
- dispersed: analysts scattered across organization, little coordination
- Hire right people! “Professionals who can deliver data-backed insights that create business value — and not just crunch numbers — are the lifeblood of an Insight-Driven Organization”
- strong quantitative skills
- strong biz & content skills (understand content and context)
- strong data modeling & management skills
- strong IT skills
- strong creative design skills (yea: techies often overlook the cool design guys & gals)
- Change the mindset (critical, IMHO!):
- Communicate: build compelling picture of future to steer people in right direction.
- Advocate: develop cohort of leaders to advocate for program.
- Active Engagement: engage key figures to create pull for the program
- Mobilize: mobilize right team across the organization.
- How do you actually do it?
- improve insight-to-impact with “Exponential Biz Processes” — must rebuild existing business processes! Involves digital user experience, biz process management, enterprise science, all data, and IT modernization.
- re-engineer processes from ground up
- develop intuitive, smart processes
- enable exception-based management
- improve insight-to-impact with “Exponential Biz Processes” — must rebuild existing business processes! Involves digital user experience, biz process management, enterprise science, all data, and IT modernization.
- Data:
- “dark data:” digital exhaust, etc. might be hidden somewhere, but still actionable.
- they use it for IoT: predictive personalization (not sure I get that straight…).
- want to have well-defined data governance organization: standards, data quality, etc.
- “dark data:” digital exhaust, etc. might be hidden somewhere, but still actionable.
- Technology: digital core (workforce engagement, big data & IoT, supplier collaboration, customer experience
- HANA
- Switch to digital delivery: visualizations are key!
- allow for faster observations of trends & patterns
- improve understanding & retention of info
- empower embedded feeds and user engagement
IoT and the Data-Driven Enterprise: Bob Mahoney, Red Hat & Sid Sipes, Sr. Director of Edge Computing, SAP
- What’s driving enterprise IoT?
- more connected devices
- non-traditional interactions such as M2M and H2M
- ubiquitous internet connectivity
- affordable bandwidth
- cloud computing
- standards-based and open-source software
- Biz benefits:
- economic gains
- new revenue streams (such as sale of jet turbine data)
- regulatory compliance
- efficiencies and productivity
- ecological impact
- customer satisfaction
- example of Positive Train Control systems to avert collisions. Now, that can be replaced by “smarter train tech”
- SAP and edge computing (can’t move all of HANA to edge, but..)
- improve security in transmission
- reduce bandwidth need
- what if connection goes down
- actual analysis at the edge
- allows much quicker response than sending it to corporate, analyzing & send it back
- keep it simple
- focused on, but not limited to, IoT
- they can run SQL anywhere on IoT, including edge: SQL Anywhere
- Red Hat & SAP doing interesting combination for retail, with iBeacons, video heat map & location tracking: yields real insights into consumer behavior.